Intelect Focus Shockwave Therapy
Whitley Chiropractic
Common Questions Answered
What is the Intelect focus shockwave treatment?
 The focused shockwave causes deep cell stimulation that releases growth factors responsible for tissue regeneration and the initiation of healing processes in the damaged tissues. It is a gold standard treatment for deep-lying tendinopathies, calcifications, and delayed bone healing conditions, such as pseudarthrosis. It can relieve pain and promote healing of injured tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues. It accomplishes this by releasing growth factors in the injured tissue.
The focused shockwave causes deep cell stimulation that releases growth factors responsible for tissue regeneration and the initiation of healing processes in the damaged tissues. It is a gold standard treatment for deep-lying tendinopathies, calcifications, and delayed bone healing conditions, such as pseudarthrosis. It can relieve pain and promote healing of injured tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues. It accomplishes this by releasing growth factors in the injured tissue.
Shockwave therapy is a safe, non-invasive treatment with convincing evidence for its effectiveness from a large body of research and clinical trials. There are now multiple, randomized, double-blinded clinical trials that support the use of shockwave therapy for plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis, and calcific tendinitis of the shoulder.
How does shockwave therapy work?
This is sometimes known as its ‘mechanism of action’. Shockwave therapy uses a specialist device to deliver acoustic energy through the skin to the injured part of the body. The shockwaves are mechanical and not electric. They are audible, low-energy sound waves, which increase the blood flow to the injured area.
Shockwave therapy has two main modes of action which will help with persistent tendon pain. First the shockwaves work to desensitise nerve endings which will often give an immediate reduction in pain. Secondly, and often most importantly, the shockwaves cause controlled micro-trauma (microscopic damage) to the tissues which encourages the body to respond by increasing the blood circulation and metabolism in the affected area. This will activate and accelerate the body’s own healing response. The shockwaves can also ‘breakdown’ disorganised tissue and calcifications.
Shockwave treatment has been shown to have physiologic benefits by increasing cell permeability to create a localized inflammatory response. The energy coming into and out of the tissue increases blood flow. Causing degradation of the nerve bundle (nociception inhibition), which allows for pain modulation via the peripheral nervous system. Upgrading the physiologic process of healing by stimulating hormones and cells that are associated with a reparative process of healing.
What does shockwave therapy feel like? Is it painful?
“I tell patients that I would like for them to have less than 5 out of 10 discomfort. I call it discomfort; I don’t call it pain,” “More discomfort is sometimes felt when we are doing the acoustic shockwave closer to a bone.”
“As we treat tissue with energy, blood flow increases, so there may be some bruising with tissue. We are able to control the machine, so if we are told that the discomfort is 5 out of 10 when we start the machine, we’ll turn it down so it is more comfortable.”
Is there clinical evidence supporting the use of shockwave therapy?
There is a significant body of evidence supporting the use of shockwave therapy in many common conditions. For more information about your specific condition please use the links above.
The use of shockwave therapy for tendon issues is well supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). NICE provides national guidance and advice to improve health and social care in both NHS and private practice. It provides evidence based recommendations to guide best practice within healthcare. NICE have produced guidelines for the use of shockwave in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy, plantarfascitis and calcific tendinopathy.
In summary, shockwave therapy significantly reduced the pain that accompanies tendinopathies and improves functionality and quality of life. It has been stated that shockwave therapy has a 70% success rate for tendinopathies (Moya et al, 2018, Dedes et al 2018).
What is shockwave therapy used for?
Shockwave therapy is an effective treatment modality for a variety of lower and upper limb, neck and low back conditions. These include:
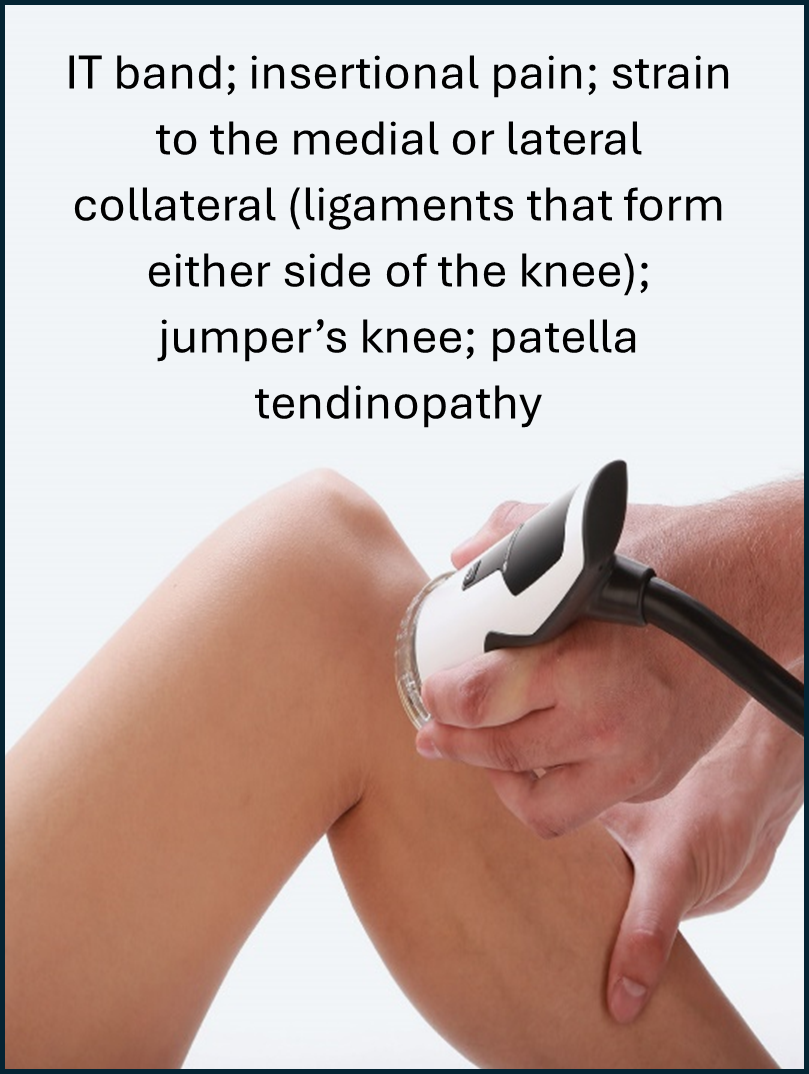
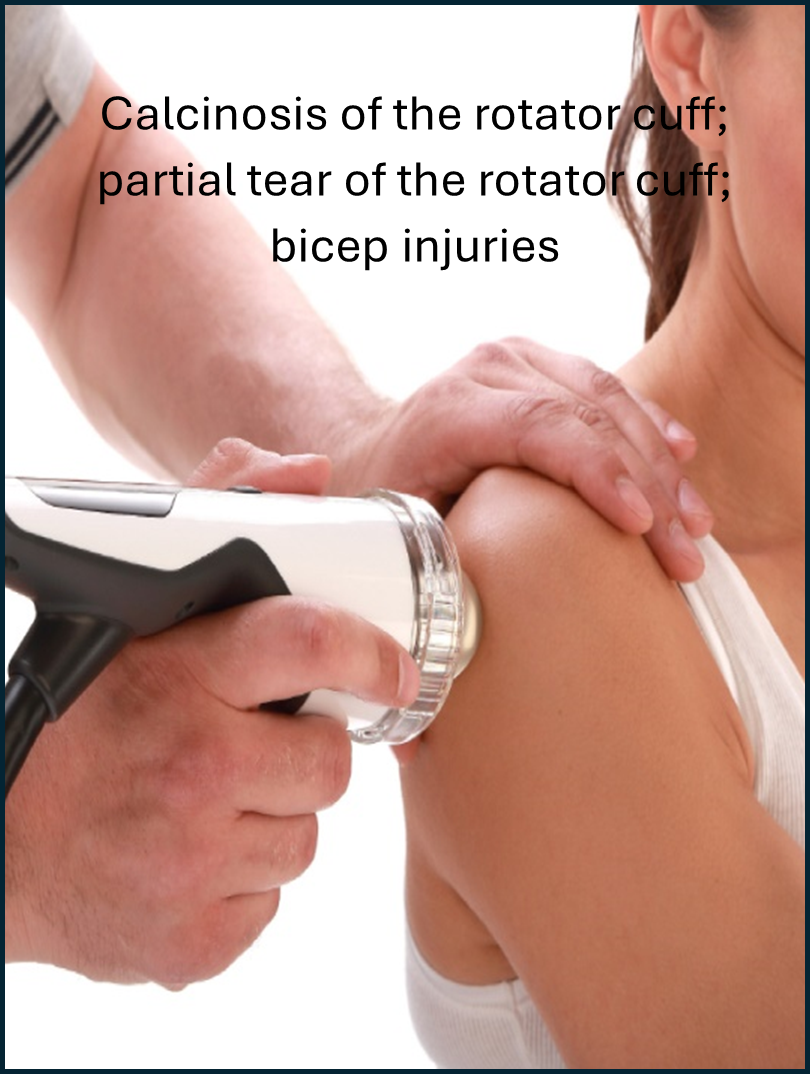
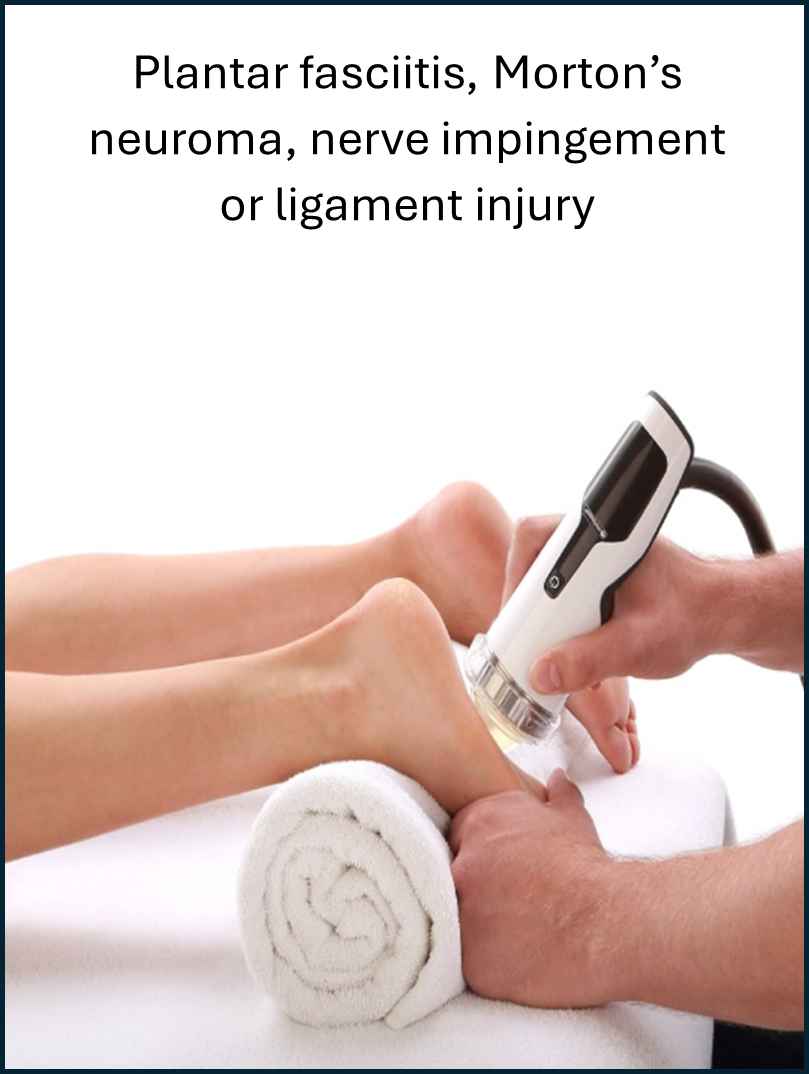
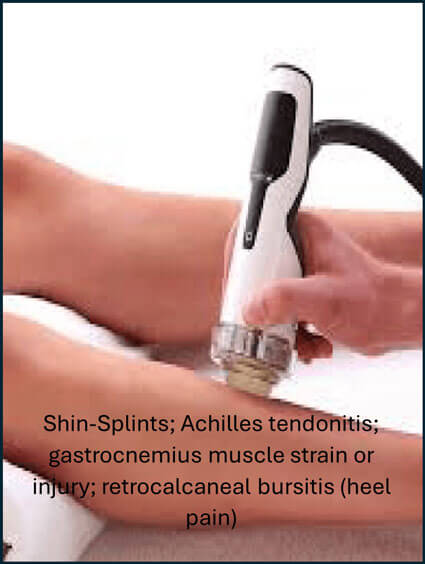
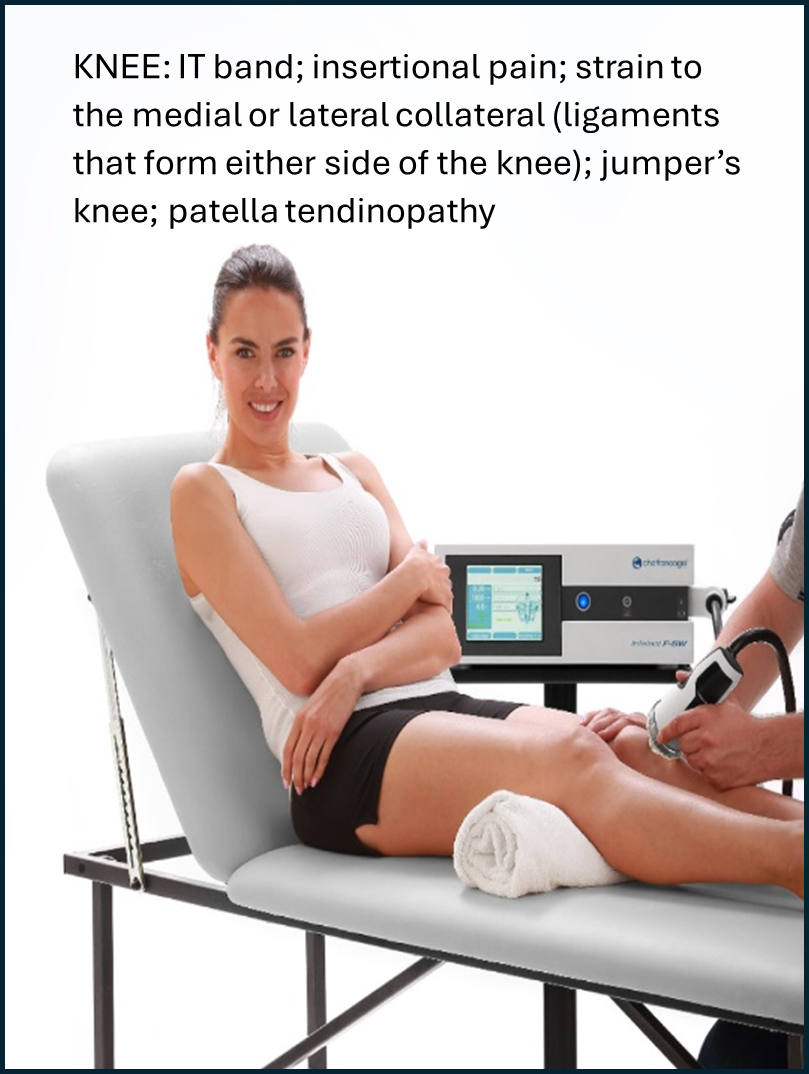

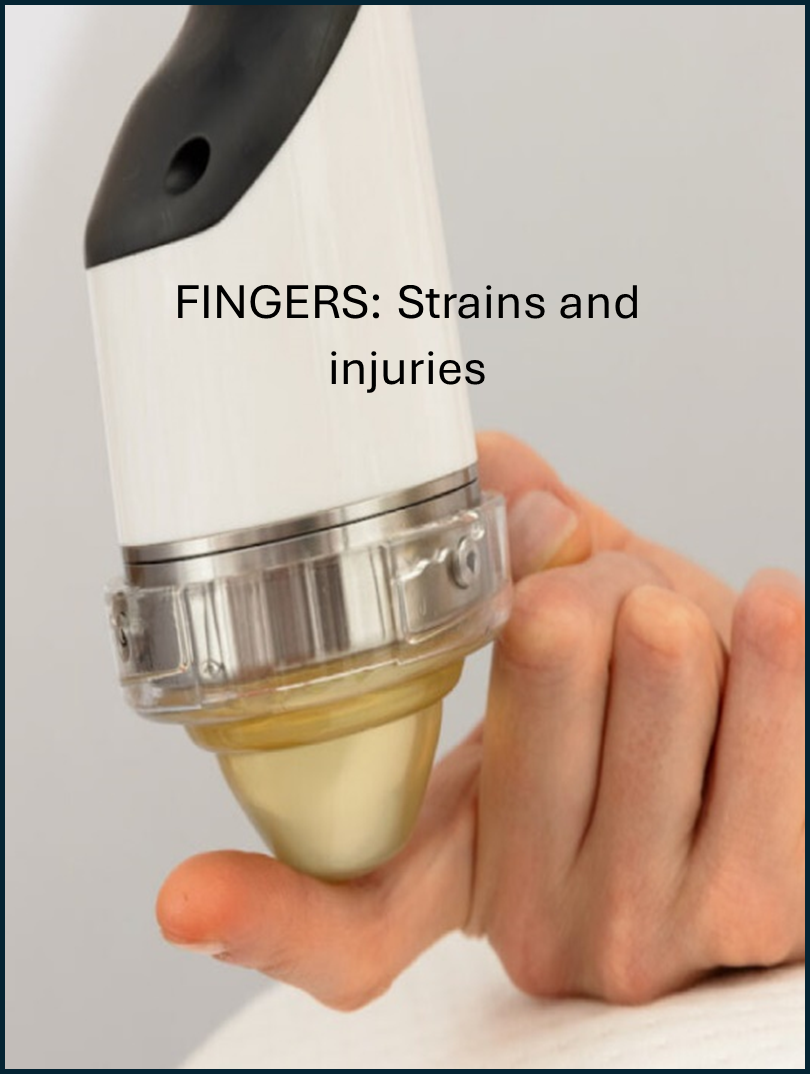
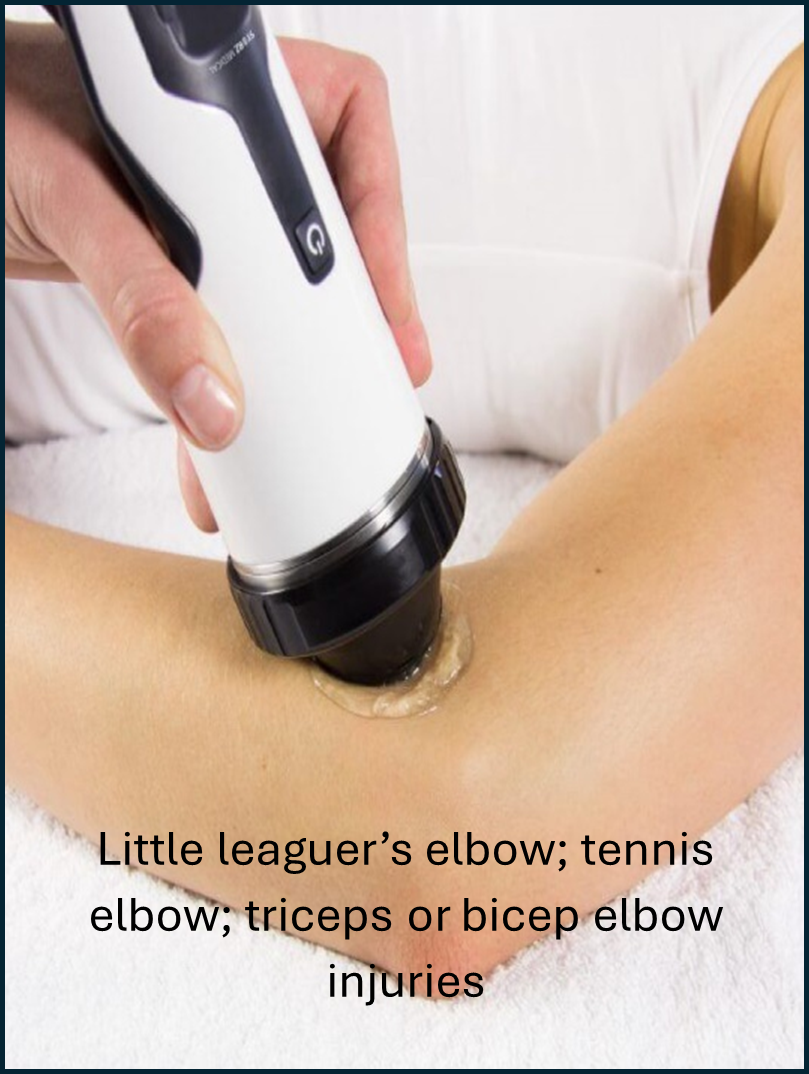
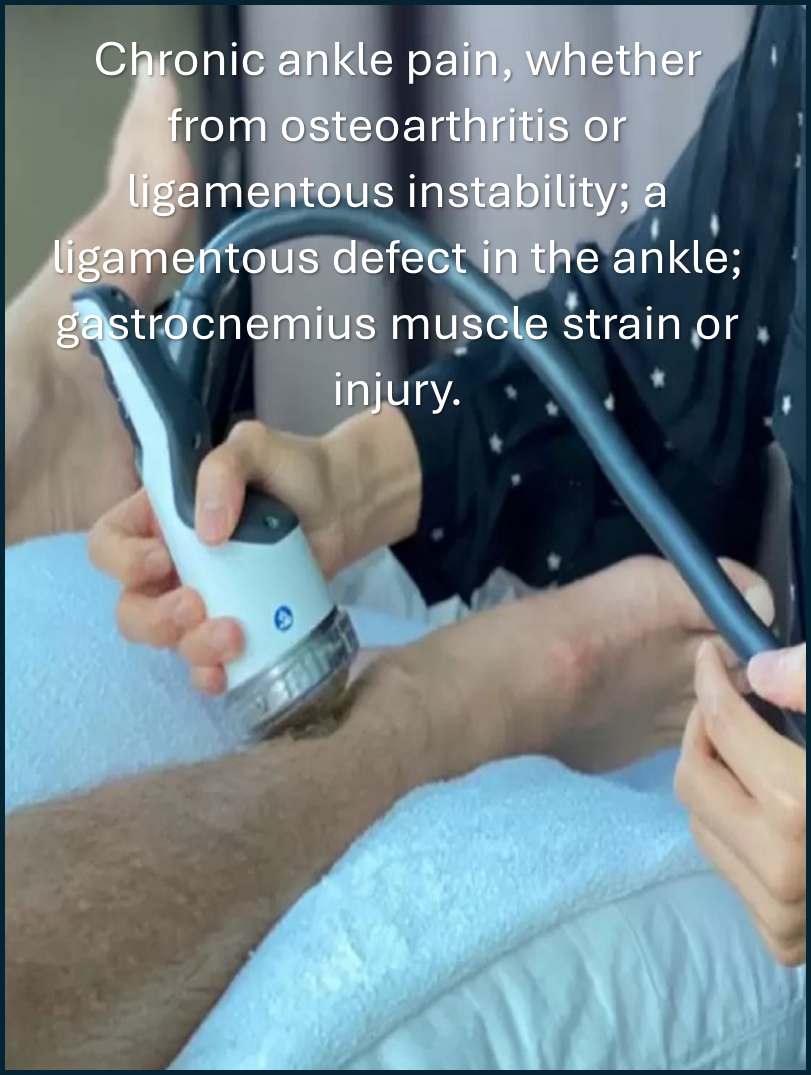
Who is a candidate for shockwave therapy?
Patients who have lingering injuries and who have not responded to time-honored methods of treatment and therapy are likely candidates.
There are a large number of patients who we see that deal with chronic or unrelenting pain from a sports or muscular-skeletal injury that may be 4 to 6 weeks in duration or it may be four months or six years in duration.
“Shockwave can handle all of that in terms of the therapeutic indication. There will be a variety of acute conditions where it may be relevant, but for the most part, these are patients who are at least four to six weeks out from the injury, and their response to therapy has yet to be realized in terms of the benefit.
Who is not a candidate for shockwave therapy?
Patients who have the following contraindications:
- Coagulation disorders, thrombosis or occlusive vascular disease
- Use of anticoagulants: Warfarin, Eliquis, Xarelto, etc.)
- Tumor disease: carcinoma, cancer patients under treatment
- Pregnancy
- Polyneuropathy, in the case of diabetes mellitus
- Acute inflammation associated with an infection
- Children with open-growth plates

